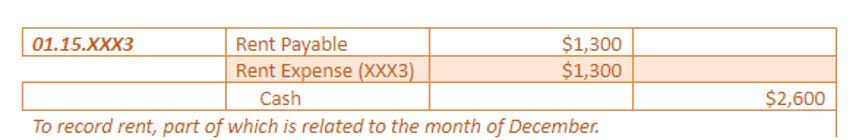
This provides investors and stakeholders a complete overview of the parent company and its subsidiaries. Addressing these challenges requires a deep understanding of accounting standards, attention to detail, and a robust consolidation process. It’s important to note that the choice of consolidation method impacts the presentation of the consolidated financial statements and the recognition consolidated meaning in accounting of intercompany transactions. Each method has its own advantages and limitations, and the selection should align with the specific circumstances and requirements of the parent company and its subsidiaries. Consolidated accounts represent a set of accounts that combines the financial results of a group of entities, rather than showing the results of each entity separately.
The parent company’s balance sheet lists all of the business’s assets and income or costs. Key financial reports generated from preparing consolidated financial statements include the income statement, balance sheet, and statement of cash flows. The consolidated financial statement should reflect the combined equity investments, liabilities and net worth of all entities included in the consolidation process. Finally, accountants must ensure that reported revenues or expenses are not double-counted when completing this task. It should address the necessary steps to prepare consolidated financial statements, including compiling subsidiary accounts into a parent company’s financial statements. It is a type of consolidation accounting that combines two or more companies’ financial results and assets into one set of financial statements.
About the IFRS Foundation
An example would be two separate software engineering teams coming together after consolidation. For example, a fast-growing business may want to acquire another company that requires additional funding and staff. Still, the existing resources should be spread more evenly across other operations and products. For example, a software company may have subsidiaries in various countries and use foreign currencies.

Under the equity method of consolidation in the financial consolidation process, the parent company reports the investment in the subsidiary on the balance sheet as an asset that is equal to the purchase price. Then when the subsidiary company reports its net income, the parent company reports revenue equal to its share of the subsidiary’s profits. Consolidated financial statements provide a comprehensive overview of a parent company and its subsidiaries as if they were a single economic entity. By combining the financial results of a parent and its subsidiaries, these statements offer valuable insights for corporate finance decisions.
Transitioning from GAAP to IFRS: Considerations for Consolidated Financials
Given that it is easier to demonstrate relative power over a legal entity than absolute power over it, the VIE model may result in consolidation more often than the voting interest entity model. The equity investors at risk, as a group, lack the characteristics of a controlling financial interest. Overall, consolidating accounts payable offers numerous benefits to organizations looking to save money or increase efficiency in their accounting processes. Additionally, consolidation ensures the uniformity of accounting principles across all operations and facilitates comparison with competitors or industry standards.
This provides greater transparency into the overall financial health and performance of the consolidated group of companies. Despite the challenges, consolidation remains an essential process for providing a comprehensive view of a company’s financial performance and position. By identifying and addressing these challenges, companies can strengthen their consolidation processes and enhance the accuracy, transparency, and reliability of their consolidated financial statements. The process of consolidation begins by gathering the individual financial statements of each subsidiary company. These statements include the balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement, and statement of changes in equity. The financial statements are then adjusted to eliminate any intercompany transactions, which can mask the true financial position of the group.
Consolidated Accounts: Introduction
Equity consolidation is a critical aspect of accounting for companies with multiple owners. An example of equity consolidation comes from ABC Corporation, formed by three industrial partners who each owned 33% of the company’s shares. Due to their ownership structure, the partners had to consolidate their respective equity interests to accurately report the financial position and performance of ABC Corporation. The purpose of consolidation is to present information about the performance and position of all companies within the parent company’s economic environment as one monetary unit. It allows investors to understand better how well the parent company manages all its subsidiaries together rather than viewing them separately.